Diabetes
The data regarding diabetes in the world are very worrying. Sedentary lifestyles, unbalanced diets and other factors have contributed to making this disease a global pandemic which affects more than 380 million people and will affect more than 500 million in 15 years.
What is diabetes or diabetes mellitus?
Diabetes mellitus is a disease characterised by the high level of glucose in the blood stream resulting from defects in the capacity of the body to produce or use insulin.
Insulin helps glucose enter into the cells, where it is used to generate energy.
When glucose accumulates in the blood instead of entering the cells, it can produce complications.
Insulin is prescribed to many people with diabetes, whether because their body does not produce insulin (type 1 diabetes) or because it does not use insulin properly (type 2 diabetes).
Types of diabetes
There are different types of diabetes. Mainly we can talk about 3:
- type 1 diabetes
- type 2 diabetes
- gestational diabetes
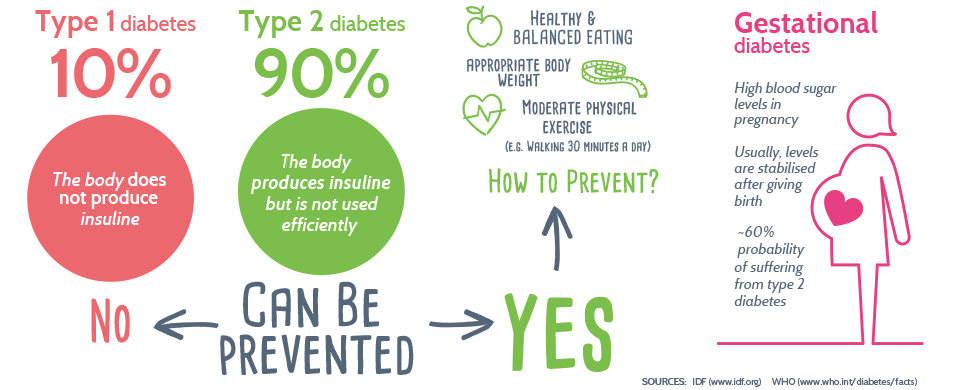
Type 1 diabetes:
Generally diagnosed in children and young adults, in this type of diabetes the pancreas does not produce insulin. Only 5-10% of people with diabetes have this type. With the help of therapy, with insulin and other treatments, patients with type 1 diabetes can control their disease. Type 1 diabetes CANNOT be prevented.
Type 2 diabetes:
Type 2 diabetes is the most common diabetes, and it can be prevented. The body of a person with type 2 diabetes does not produce sufficient insulin or the cells do not make use of the insulin. Almost a third of people with type 2 diabetes are unaware that they have the disease. Many find out that they have diabetes when they face a problem such as blurred vision, heart problems, or chronic fatigue. Prevention of type 2 diabetes is vital, as is periodically checking blood glucose levels, above all when irregularly elevated levels begin to be detected.
Prediabetes
Prediabetes is a disorder in which the level of glucose in the blood is greater than normal but not high enough to be considered diabetes. People with prediabetes have a high probability of developing type 2 diabetes. The majority of people with prediabetes do not know they have it until it is too late. An important step in its prevention it to know about it.
Type 2 diabetes can be prevented
Discovering our genetic predisposition to suffering from it can motivate our determination to improve our eating habits and physical exercise habits, which are necessary but also sufficient to prevent it.
Find more about type 2 diabetes
Results that indicate prediabetes*:
- Level of glucose in the blood when fasting of 100-125 mg/dL
- Glucose in the blood, 2 hours after eating sugar, of 140 mg/dl – 199 mg/dL
- An A1C glycated haemoglobin level of 5.7% to 6.4%
- A Quantose IR (insulin resistance) level of 63 or higher
(*These data are informative. Consult your doctor)
Gestational diabetes:
Many women suffer from gestational diabetes during pregnancy. Gestational diabetes can cause the baby to be born with a greater weight than usual and other complications if it is not controlled adequately. Those complications can be avoided with a controlled diet during pregnancy.
Gestational diabetes also increases by 60% the risk of the mother to suffer from type 2 diabetes later on, throughout her life.
Find out more about gestational diabetes
Complications of diabetes
Diabetes can have an enormous impact on your lifestyle. Some people are capable of controlling diabetes by means of diet and physical exercise, but many others , require daily medication, as well as continuous monitoring of the levels of glucose in their blood.
Uncontrolled diabetes can result in serious complications such as blindness, heart failure, brain haemorrhage, kidney failure or partial amputations of the lower extremities, among others.
Find out more about the complications of diabetes


